Difference between revisions of "Anti roll bar"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Anti Roll Bar) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[Image:dower_at_snetterton.jpg|thumb|left|Martin gets his inside front wheel off the deck at Snetterton]] | |
| − | + | The primary function of '''anti roll bars''' is to reduce body roll by adding to the roll resistance of the springs. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
The anti-roll bar reduces body roll to keep the suspension geometry, and ultimately the tire, parallel with the road. | The anti-roll bar reduces body roll to keep the suspension geometry, and ultimately the tire, parallel with the road. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 13: | ||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sway_bar Wikipedia on Anti Roll Bars] | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sway_bar Wikipedia on Anti Roll Bars] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Suspension]] | ||
Revision as of 12:39, 29 January 2007
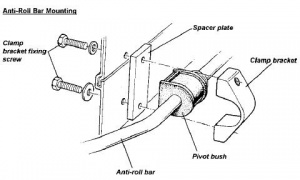
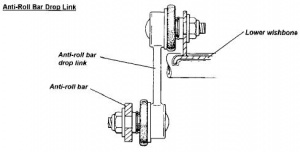
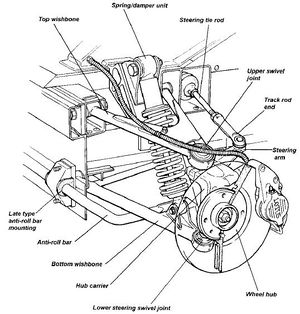
The primary function of anti roll bars is to reduce body roll by adding to the roll resistance of the springs.
The anti-roll bar reduces body roll to keep the suspension geometry, and ultimately the tire, parallel with the road.
Stiffer bars reduce body roll more, but too stiff a bar can deteriorate independent suspension performance, and ultimately cause an inside tire to lift off the ground during hard cornering.